Beyond Earth: India's Soaring Space Odyssey
Explore India's economic leap through space exploration!
Summary:
Introduction
What is the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)?
ISRO Projects
Chandrayan Program
Missions:
The Rise of Chandrayan
Bharatiya Antariksha Station
Space Exploration Economic Impact on India
Government Investments in Space
Job Creation and Education Improvements:
ISRO Partnerships:
Commercialization of Space Activities:
Conclusion
Introduction
Over the past 15 years, the Indian economy has thrived, boasting an average Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of around 6.17% from 2006 to 2023. This economic prosperity has not only enhanced the quality of life but has also spurred increased government investment, notably in the scientific sector, including the space program—the main focus of this article.
Src: Statista
What is the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)?
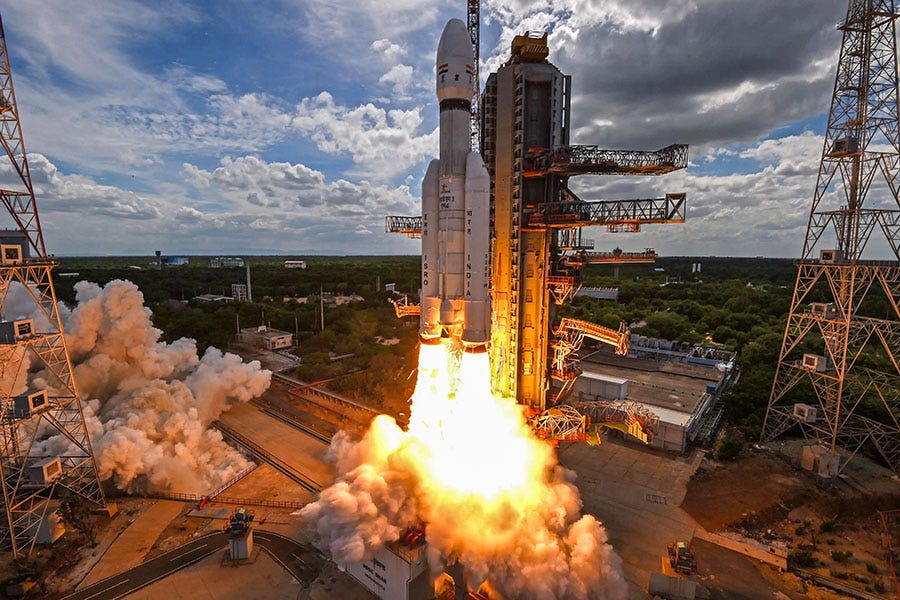
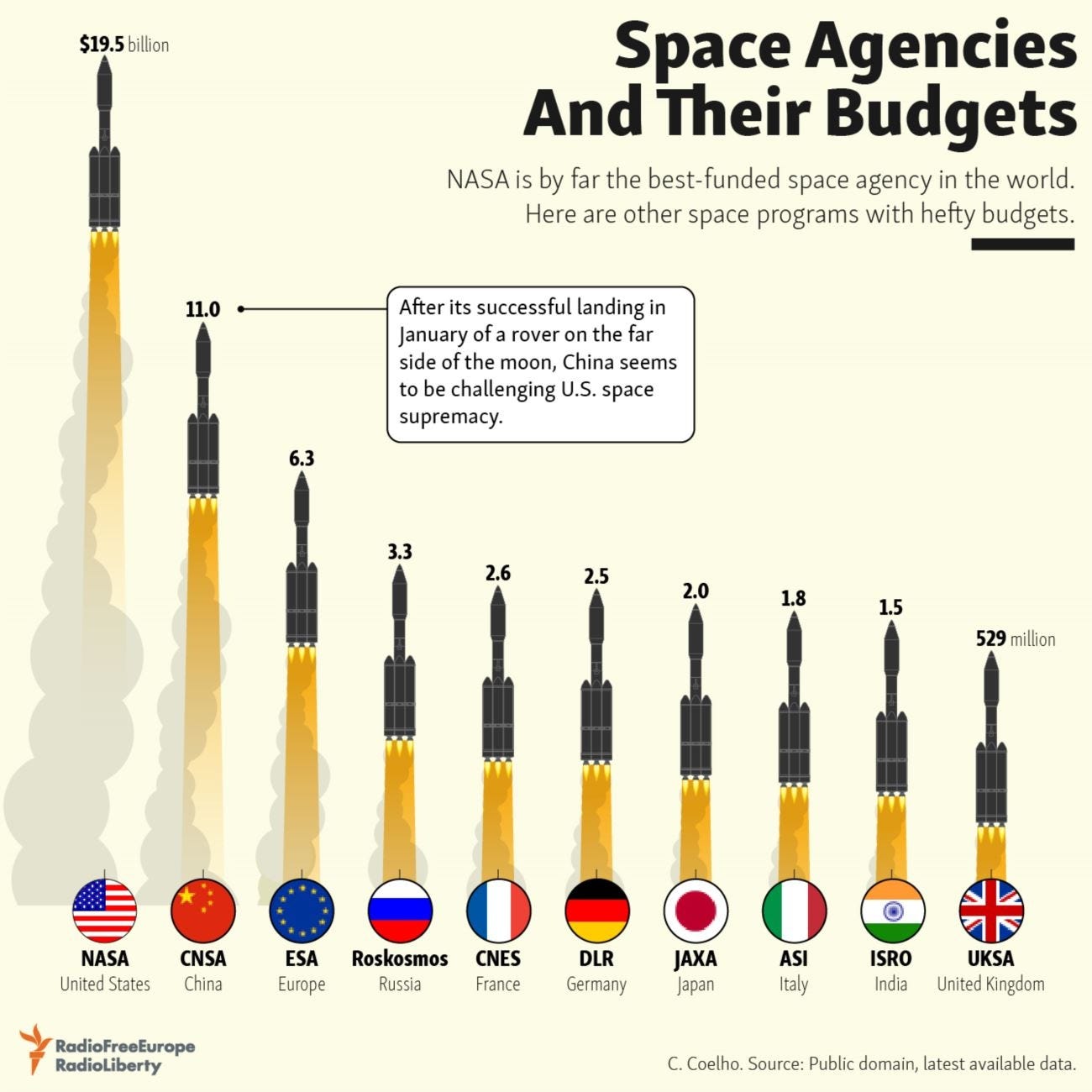
The recent successful landing of the Chandrayaan-3 Lander Module on the moon on July 14, 2023, marks a significant milestone for ISRO. The Indian government has responded by escalating its space expenditure investments from $960 million in 2017 to an anticipated $1.5 billion in 2024. Before delving into the heart of the matter, it's crucial to outline the origins of ISRO, which emerged in the 1960s and was officially established in 1969. As an integral part of the Indian Space Department, ISRO's mission encompasses the creation of launchers, satellites, scientific programs (e.g., the Chandrayan program for the moon), and military satellites. ISRO's unique approach involves not only designing space missions but also manufacturing launchers, propulsion systems, satellites, and instruments in-house. This self-reliance has led to a workforce of over 18,000 people in 2020, a figure rivaling NASA's employee count. ISRO's budget reached 2 billion euros in 2022.
The prime objective of ISRO is to develop space technology and its application to various national needs. (Isro)
Src: The statesman
ISRO Projects:
Chandrayan Program
Initiated on August 15, 2003, the Chandrayan Program aims to explore the moon using robots and conduct satellite exploration of other planets in the solar system. This major ISRO program has drawn comparisons to China's Chang'e program, echoing the space race dynamics of the 1960s.
Src: Journaldugeek
Missions:
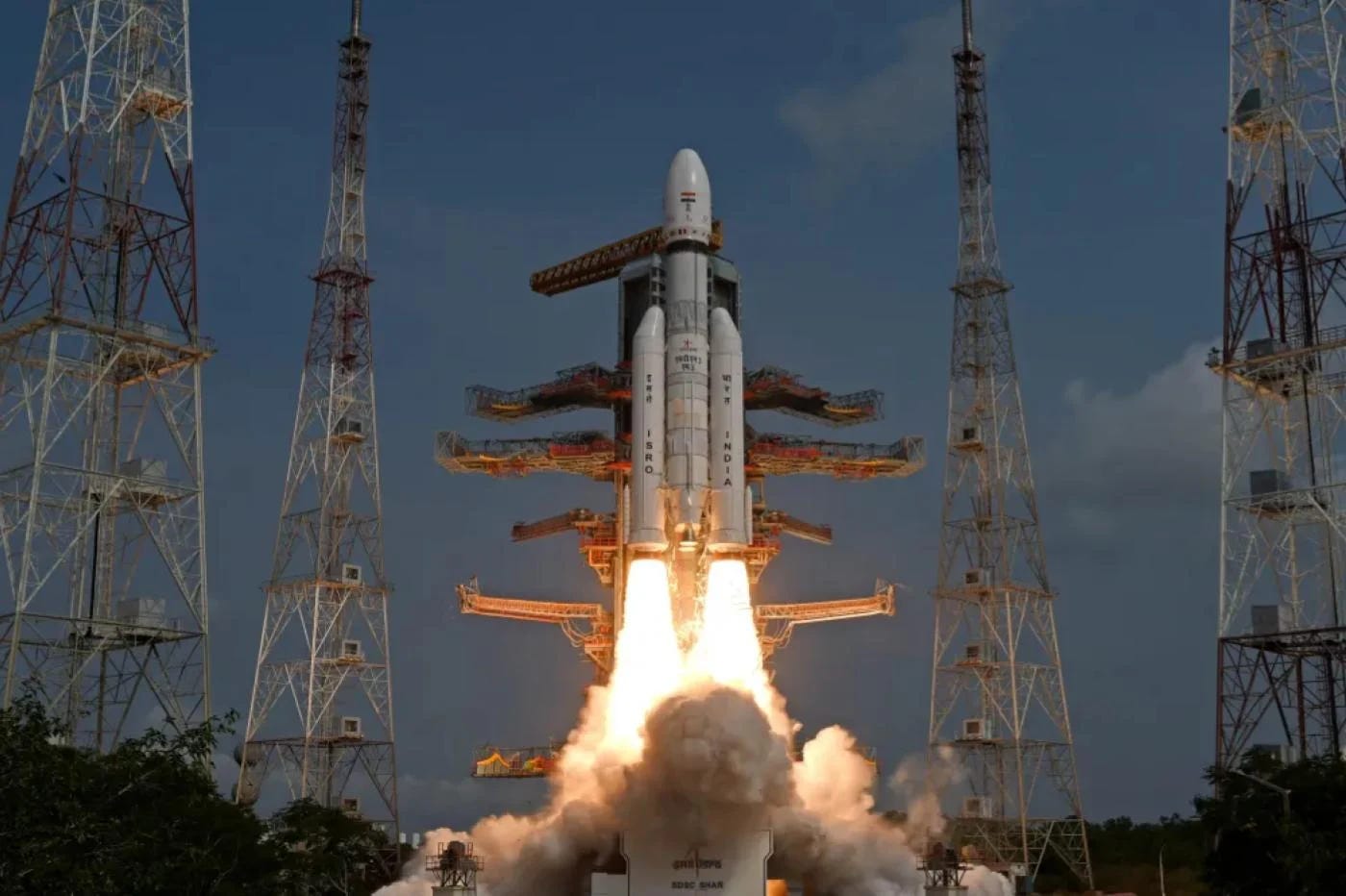
Chandrayan's first mission, Chandrayaan-1, launched in October 2008, mapping the moon's surface with extreme precision until its abandonment in August 2009 after fulfilling most objectives.
Despite the failure of Chandrayaan-2's rover landing in July 2019, the orbiter remains functional, establishing communication with Chandrayaan-3.
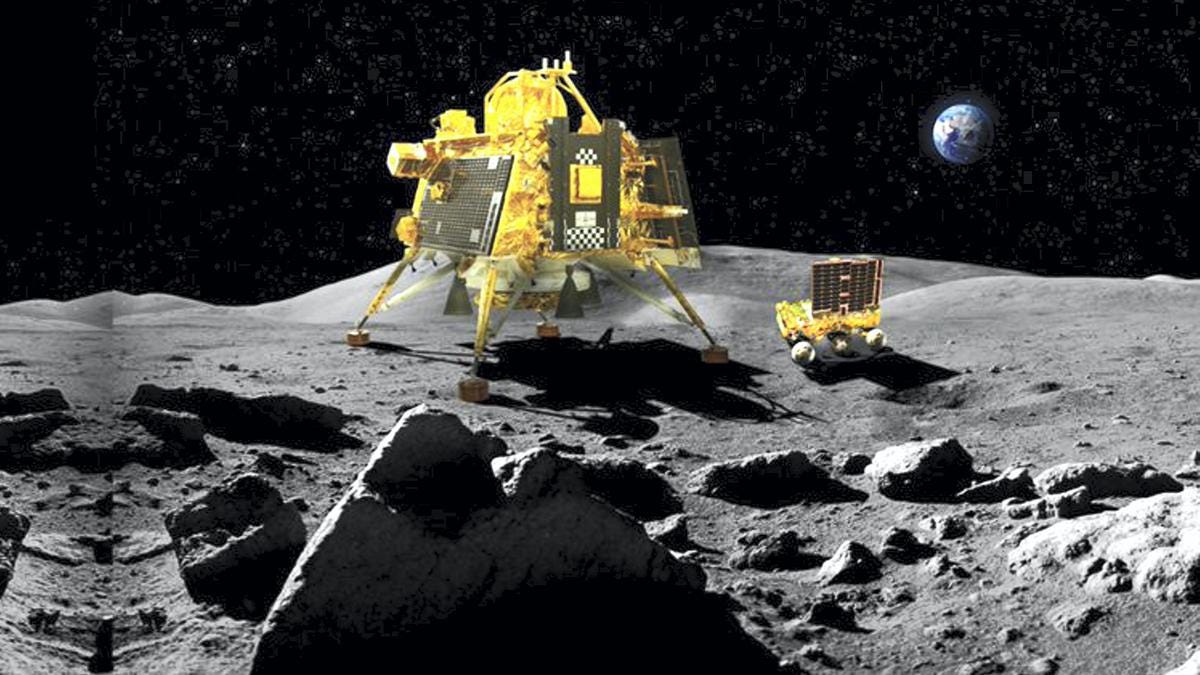
Launched on July 14, 2023, Chandrayaan-3 successfully landed its rover on the moon's south pole on August 23, making India the fourth country to achieve this feat. Notably, Chandrayaan-3 returned to the high orbit of Earth on December 4th, 2023.
Rumors suggest ISRO's plans for a sample return mission, Chandrayaan-4, in collaboration with JAXA, featuring a Japanese Rover and an Indian Lander, expected to launch no earlier than 2026.
Src: Aerospatium
India is the first nation to successfully land a spacecraft in the lunar south pole region (Wikipedia)
The Rise of Chandrayan:
The rapid ascent of the Chandrayan program, fueled by technological competition, particularly with China, mirrors India's economic rise over the past two decades. Strong collaborations with space agencies like JAXA have been pivotal in its success, marking the program's emergence onto the global stage.
Bharatiya Antariksha Station:
The Bharatiya Antariksha Station, intended as a space station operated by ISRO, was initially planned for 2030 but faced delays due to the COVID-19 pandemic and technical challenges. Despite its early stages, this project underscores India's commitment to ambitious space exploration, reflecting a long-term vision. Noteworthy is NASA's expressed readiness to support India's goal of building a space station, emphasizing potential collaboration and innovation.
Src: India Today
Space Exploration Economic Impact on India
Government Investments in Space:
India's space budget is around $8 billion, just two percent of the total. IN-SPACE (Indian National Space Authorization Centre) aims to raise this to 8% by 2033 and 15% by 2047. In 2022, the government allocated over 124.7 billion Indian rupees, with plans to increase it to 125 billion in 2023. India's space spending as a share of GDP is low compared to the US (0.28%), Russia (0.15%), ranking seventh globally at 0.04%. India's moon mission cost around $74 million, less than half of Russia's ($200 million) and NASA's estimated rover budget ($433.5 million).
Src: Mashable India
"India has the capability to travel to the Moon, Mars, and Venus, but we need more investment for the space sector to develop, fostering the nation's overall growth."
Job Creation and Education Improvements:
Apart from ISRO, there are six other space agencies in India, including Antrix Corporation Limited. These space activities have generated jobs for approximately 45,000 people. For comparison, NASA has just under 18,000 civil servants.

Src: The New York Time
ISRO Partnerships:
ISRO has formal cooperative agreements with several dozens of countries. Notable partnerships include collaboration with Amazon Web Services (AWS) India Private Limited for space-tech innovations through cloud computing. NASA and ISRO have formed a joint working group for human space flight, exploring cooperation in various studies. India's collaboration with Russia in the space sector is longstanding.
Src: LinkedIn
Commercialization of Space Activities:
India currently holds a modest 2% share in the global space economy. IN-SPACe aims to increase this to 8% by 2033, targeting $11 billion in exports over the next decade. India's space sector is recognized for cost-effective satellite launches, successful Mars probes, and carrying numerous foreign satellites into space. To achieve the $100 billion target by 2040, India needs clear regulations, promotion of foreign investments in satellite establishments, and the use of schemes like production-linked incentives (PLI) to establish itself as a manufacturing hub in space exploration.
Src: Research Gate
Conclusion:
The Indian Space Program not only symbolizes India's technological prowess and achievements in space exploration but also serves as an economic driver. With government investments, job creation, educational advancements, and strategic partnerships, ISRO plays a multifaceted role in shaping India's position in the global space arena. As India charts its course for the future, navigating both lunar exploration and the establishment of a space station, the economic impact of these endeavors will likely continue to be a significant aspect of the nation's growth story. As India seeks to increase its share in the global space economy, the coming years promise exciting developments and opportunities for economic expansion and technological innovation.
The Gaganyaan programme aims to send four astronauts into space for a three-day mission in 2025 and bring them back safely to Earth. (India Time)
Src: Forbes India
How do you envision the intersection of India's space exploration and its economic trajectory in the coming decades?
let me know in the comments.
Dive Deeper: Unlock Insights with Recommended Articles on the Indian Space Program:
If you have inquiries about the finance, business, geopolitical and economic realms, the article crafting process, or suggestions for future topics, don't hesitate to reach out. Your support is valued and appreciated.
Src: Wikipedia & Spacenews & Wikipedia & ESA & Wikipedia & CNBC & Wikipedia & Wikipedia