Beyond Borders: Navigating the Trillion-Dollar Seas of Global Shipping
Sail through the evolution of global shipping – from 35 cents to trillions. Explore the industry's growth, challenges, and eco-friendly horizons.
Summary:
35 Cents: Charting the Seas of Growth in the Shipping Industry
The Rise in Seaborne Trade: A Financial Odyssey
China's Commanding Role: The Shipbuilding Powerhouse
Sailing Through History: The Evolution of Maritime Transportation
Current State and Major Players: Navigating Challenges
Technological Waves: Sailing into the Future
Sustainability: Navigating Towards Greener Seas
Conclusion: Sailing Ahead in the 21st Century
35 Cents: Charting the Seas of Growth in the Shipping Industry
Over the last decade, the shipping industry has navigated tumultuous waters, experiencing unprecedented growth and overcoming substantial challenges. The journey from 35 cents – the cost to ship a Nike shoe from China to the USA – to becoming a trillion-dollar industry is a tale of resilience, innovation, and global dynamics.
Src: Oregon Live
Nike made the decision to transport their products on cargo ships instead of using airplanes. This new way of transporting their products claimed to have saved Nike over $8 million in one year. By this change in transportation, Nike projects their reduced carbon footprint to have decreased by 30% in 2020. (justtradeplnu)
The Rise in Seaborne Trade: A Financial Odyssey
Seaborne trade, the backbone of global commerce, has seen remarkable growth. From 1990 to 2021, cargo volume more than doubled, reaching nearly 11 billion tons. The capacity of the worldwide merchant fleet grew by 43% between 2013 and 2021, hitting almost 2.1 million deadweight tons in 2021.
Src: Visual Capitalist / world bank
The impact of COVID-19 on the industry, causing closures, congestions, and labor shortages, was substantial. Despite the disruptions, the industry weathered the storm, reporting record-high profits of $208 billion in 2022, nearly double the 2021 figures.
The COVID-19 pandemic showed a remarkable effect on the shipping markets in 2020. According to Clarksons Shipping Intelligence Network (2020a) estimations, global seaborne trade would contract by 4.4% across 2020, a comparable decrease to that seen after the international financial crisis (2009: 4.1%). (Nih.gov)
China's Commanding Role: The Shipbuilding Powerhouse
China has emerged as a titan in shipbuilding, dominating the industry since 2010. Home to the busiest container ports globally, it exports bulk carriers, oil carriers, and container ships. With approximately 5,600 container ships in the global fleet as of December 2022, China shapes the industry's landscape.

I recommend that you check out this article by Visual Capitalist to visualize China's dominance in the cargo shipping industry:
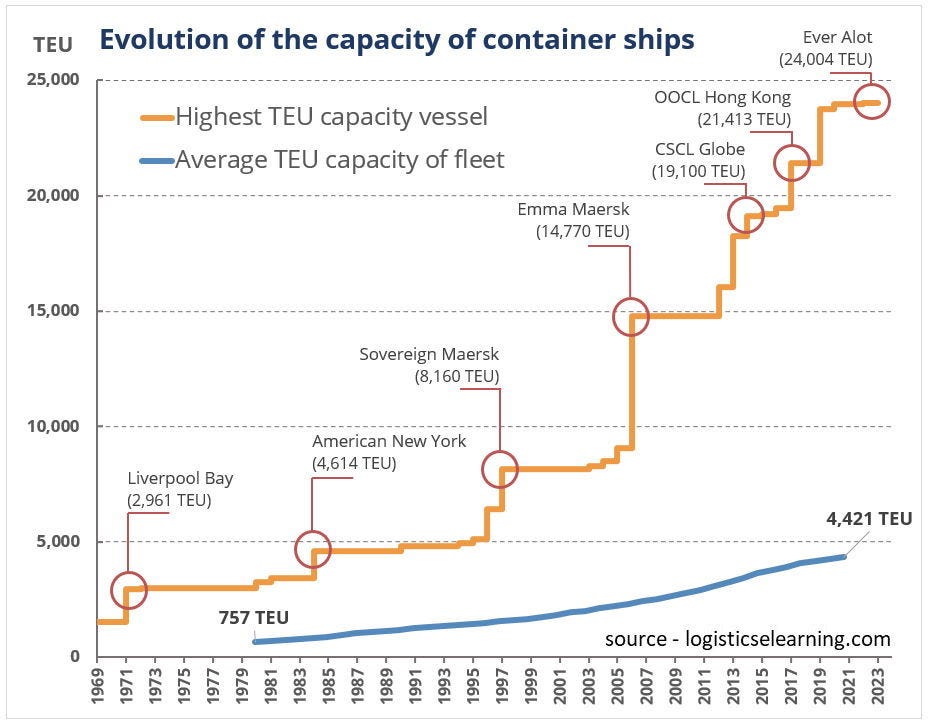
Sailing Through History: The Evolution of Maritime Transportation
The shipping industry's roots trace back to ancient civilizations, with significant technological leaps occurring over the centuries. From wooden sailing ships to steamships and modern internal combustion engines, the industry continually adapted. Containerization in the mid-20th century revolutionized global trade, propelling major companies like Maersk, MSC, and CMA CGM into influential roles.
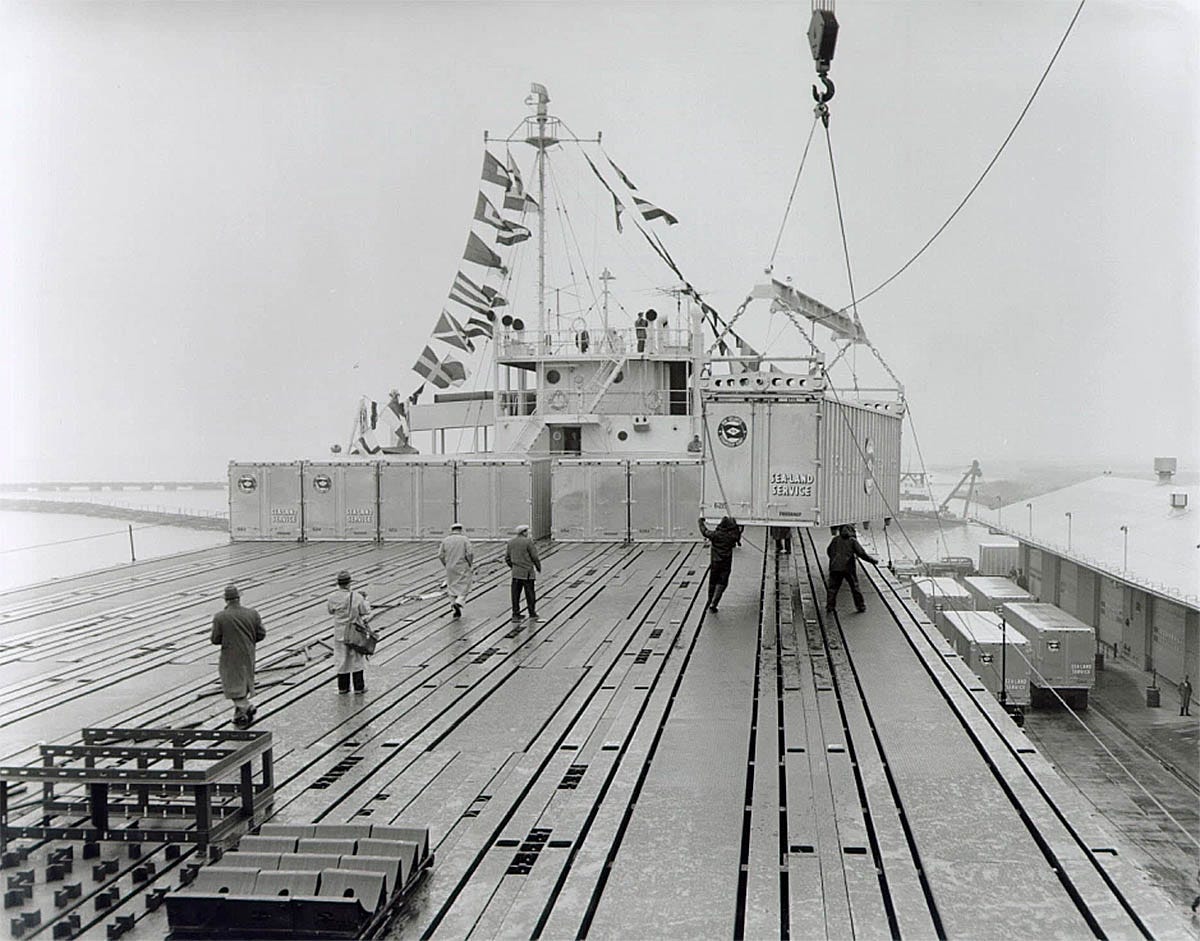

Src: inboxprojects
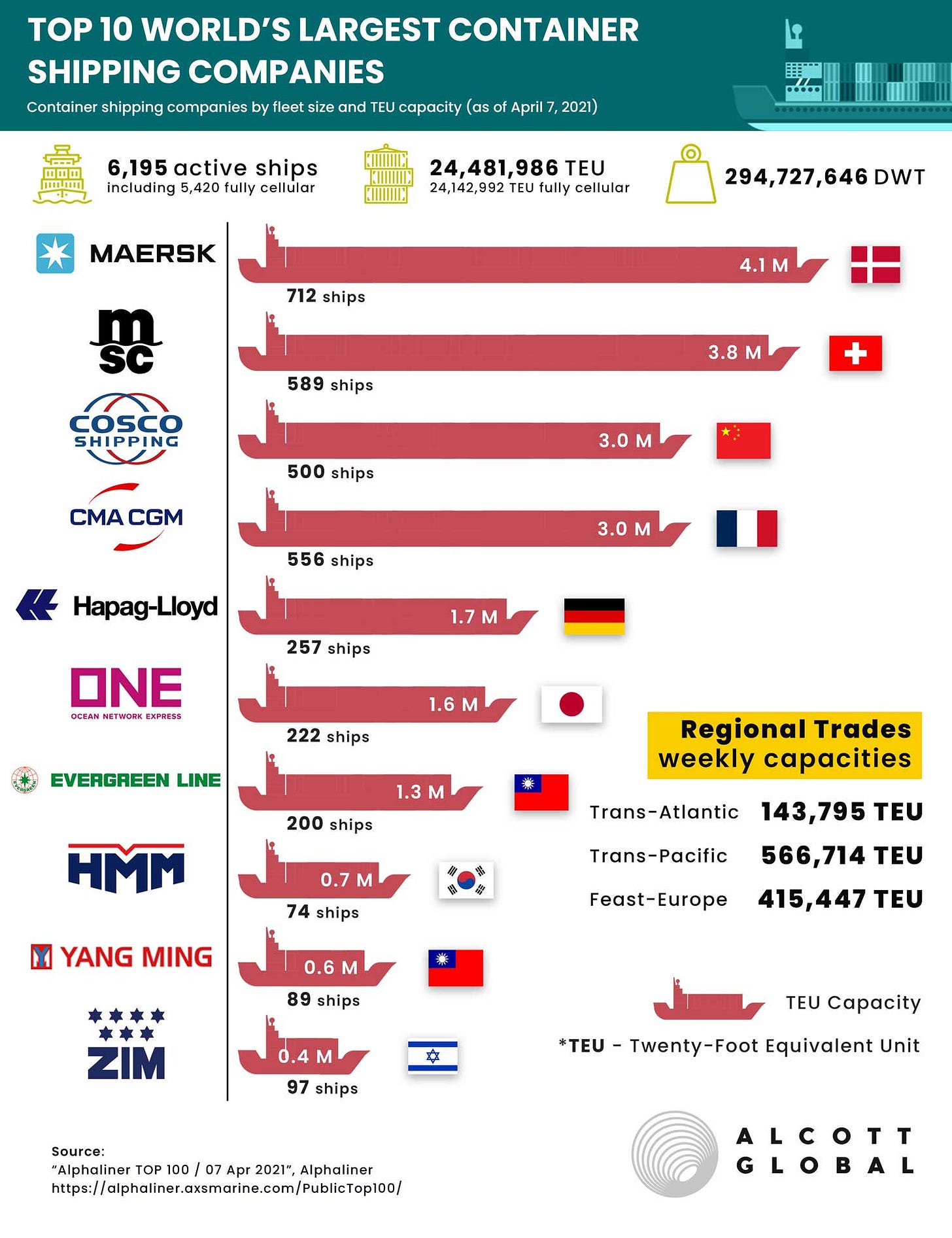
Current State and Major Players: Navigating Challenges
In 2021, seaborne trade volume surpassed 11 billion metric tons, nearly tripling the 1990 figures. The container shipping industry is projected to reach $12.52 trillion by 2028. Major players, including Maersk, MSC, and CMA CGM, dominate segments like container, bulk, and tanker shipping.
Src: Alcott Global
The COVID-19 pandemic presented unprecedented challenges, disrupting supply chains and causing fluctuations in demand. Despite facing economic fluctuations, geopolitical tensions, and environmental challenges, the industry demonstrated remarkable resilience.
Technological Waves: Sailing into the Future
Technology, a powerful force in maritime trade, has ushered in digitalization and automation. From advanced communication systems to autonomous vessels, the industry undergoes a transformative era. Digitalization enhances operational efficiency, while automation, from port terminals to autonomous vessels, reshapes shipping operations, increasing productivity and safety.
Sustainability: Navigating Towards Greener Seas
As environmental concerns mount, the industry is steering towards sustainability. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) sets ambitious targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Initiatives include using cleaner fuels, adopting energy-efficient technologies, and exploring alternative propulsion systems.*
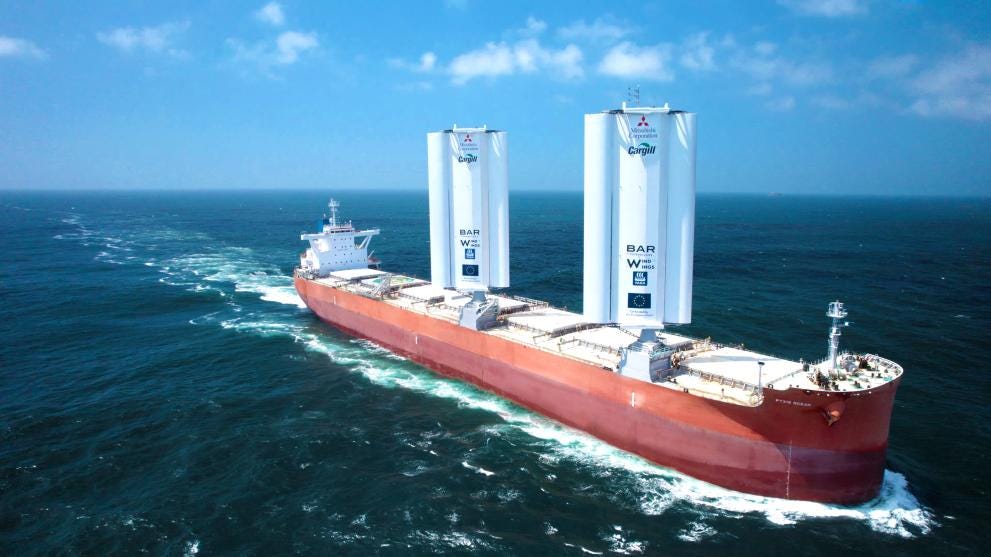

Src: European Climate
The 2023 IMO GHG Strategy envisages, in particular, a reduction in carbon intensity of international shipping (to reduce CO 2 emissions per transport work), as an average across international shipping, by at least 40% by 2030. (IMO)
Conclusion: Sailing Ahead in the 21st Century
The shipping industry, vital for global trade, faces evolving challenges and opportunities. As it sails into the future, staying abreast of technological advancements, environmental responsibilities, and global dynamics is crucial. From the impact of COVID-19 to the rise of China as a shipbuilding giant, the industry's journey from 35 cents to trillions unfolds with lessons for those navigating its expansive seas.
The global cargo shipping market size was valued at $2.2 trillion in 2021, and is projected to reach $4.2 trillion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 7% from 2022 to 2031. (Allied Market Research)
Src: Innovez One
How can the shipping industry strike a balance between economic growth and environmental sustainability in the coming decade?
let me know in the comments.
Datas from: Statista & Shipfinex
Disclaimer: Please note that I am not a financial advisor and the information provided is my personal opinion, and should not be taken as professional financial advice.